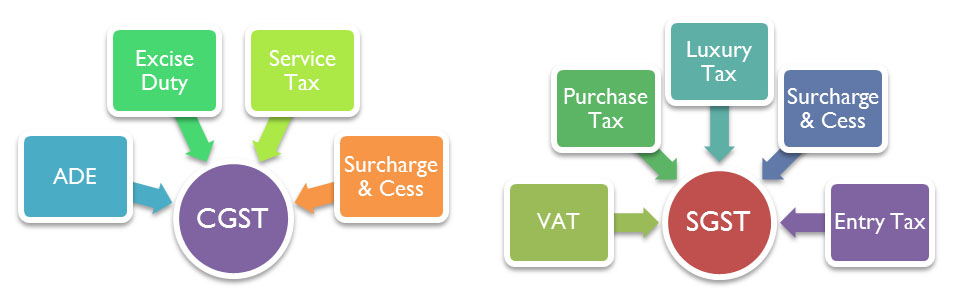
Difference between CGST SGST and IGST
Taxes subsumed under CGST SGST and IGST
Impact of GST on Transport Industries:
Fundamentally every industry is likely to get benefit from GST as it will make the overall process of taxation simpler, less bureaucratic and efficient, out of which one industry shall be Transport & Logistics. Since long back, this industry had been attracting various types oflevies due to inter-state logistic structure based on the state taxation system which made it inefficient and clumsy. The Indian transport and logistics sector is primarily categorized into various segments consisting of transportation, warehousing, freight forwarding, pool distribution, packaging solutions, inventory management, management consulting, logistics optimization, etc…
Difference between CGST SGST and IGST
No GST on Transportation of Certain Goods
Service tax is not applicable on the transport of the following goods:
- Relief material for disaster struck areas (food for flood victims etc.)
- Defense or military equipment
- Newspaper or magazines registered with the Registrar of Newspapers
- Railway equipment or materials
- Agricultural produce
- Milk, salt and food grain including flours, pulses and rice
- Organic manure
No GST on Transportation of Certain Goods
As proposed under GST, movement of goods worth more than Rs 50,000 within or outside a state will require applying for an E-Bill through online registration of the consignment. Tax officials are empowered to verify the validity and accuracy of the E-Bill to avoid tax evasion. Though the intent seems to be good, but due to process of multi-layered declaration it may prove to be cumbersome.
An e-way bill or a consolidated e-way bill generated under this rule shall be valid for the period as mentioned in column (3) of the Table below from the relevant date, for the distance the goods have to be transported, as mentioned in column (2):
| Sr. no. |
Distance |
Validity period |
| (1) |
(2) |
(3) |
| 1. |
Less than 100 km |
One day |
| 2. |
100 km or more but less than 300km |
Three days |
| 3. |
300 km or more but less than 500km |
Five days |
| 4. |
500 km or more but less than 1000km |
Ten days |
| 5. |
1000 km or more |
Fifteen days |